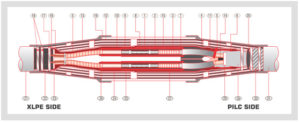
Electrical joints such as the transition joint, branch joint and cable terminations play a vital role in providing electrical connection. They physically protect the cable and offer the required mechanical support too. The terminations and the joint types are classified depending upon the function, construction materials and type of cable.
Cable termination involves connection of cable end to a device like panels, equipment or wall outlet or to another cable. Cable terminations act as via media for electrical and physical interconnecting of a cable end and a terminal or two cable ends. As far as electrical connection goes certain needs relating to current conveying capacity, voltage drop, material compatibility etc have to be fulfilled. Physical requirements include mechanical security and environmental fortification. These terminations are needed in Datacom, telecom, fiber optic and other industries.
Several methods are used for cable terminations and they differ based on the type of connector, cable type and application. The most commonly used methods are soldered connection, crimp connection, wire-wrapping connection, eye or loop connection, direct connection or compression termination. The choice of the method depends on varied factors such as whether it is meant for indoor or outdoor use, current, voltage, whether it is underground or overhead and the connector type to which the cable will be connected on the equipment.
The preparation for cable termination involves careful planning on several aspects. The various tasks comprise arranging cables based on destination, developing and dressing cables, accurate labeling and forming a connection with fiber or copper conductor. Deciding a strategy for the cable start and end and ensuring the availability of tools for completion of the job is a must. Some of the tools required in this context include the cable cutting tools, sheath removal tools, punchdown tools and so on. Cable connection is said to be complete only on proper identification and labeling of all terminations.
The work begins by determining the location of the termination point. If it is not possible to determine beforehand ensure that the length of the cable is sufficient to reach the farthermost point in the equipment room or wiring closet. The cables then should be channeled to this point checking for the sufficiency of the cable length and labeling each one of them for future identification. Forming and dressing the cables is the next step, verifying on the parallel layout of the cables and then they have to be shaped into tidy bundles with the help of loop wraps or hooks. On setting the termination area, you need to provide relief and support through appropriate cable management hardware. This is vital as a few cables have definite least bend radius requirements. It is essential for you to be aware of this fact as then the cable integrity can be maintained during its installation. This is the preparation procedure for carrying out coaxial, copper IDC or any other cable termination.
The above information gives a brief on what is involved in cable terminations and what are the preparatory steps before proceeding. As such there are several other cable accessories involved when any electrical procedure goes on and one of the names worth mentioning here is that of heat shrink products like heat shrink corrosion protection tube, heat shrink boot and so on. And all have a distinct role to play!