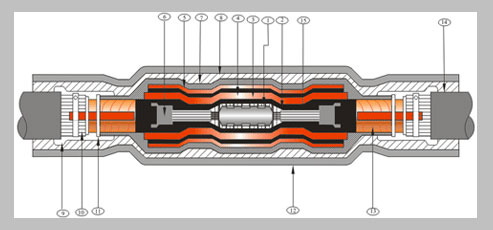
Cable joints and terminations play a vital role in providing dependable electrical connection, mechanical support and physical safeguarding of cables.They are an indispensable item in the electronic and electrical system of any household or industrial setting. The joints are categorized depending upon their function, construction materials and the cable type.
Need for Cable Joints
Cable joints act as a mode for connecting cables with varied voltages. Their shape, size and configurations differ depending upon the structure, insulation, number of cores and voltage of the cable that has to be jointed. Besides offering electrical insulation the joints give the required strength and mechanical protection to the cables. Accordingly you have the transition joint, branch joint, PILC joint used for several electrical connections which are made through different means such as soldering, crimping, using mechanical connectors and so on.
Factors Affecting the Design of Cable Joints
The factors that determine the design of the joint are
- Voltage: The voltage of the cable and the cable joint should be the same to ensure compatibility.
- Structure: The type of cable joints used will depend upon the manner in which the cables have to be connected. If two cables are to be connected at a single point then the straight through joint is a best fit while the branch joint proves suitable in a situation where many cables accumulate at one point to form a single cable thereon.
- Cores: The number of cores possessed by the cable joints has to be same as that of the relevant cables.
- Insulation: Compatibility between the cable joints and cable insulations has to be maintained. The jointed cables’ insulation can be maintained by a number of insulation procedures such as cold or heat shrinkable insulation, tape or r molded types.
Types of Power Cable Joints
There are varied types of cable joints and the difference lies in their mechanical arrangement and situations where they are required. Customized designs are quite often provided by manufacturers to suit the specific requirements of customers. Some of them are:
Branch Joint: Branch joints can be used for outdoor, indoor, underground or submerged cable jointing. It is most suited to join cables in the range of 1 to 5 cores that are polymeric, low voltage and non-shielded. These can be either ‘T’ or the ‘Y’ type.
Transition Joint:Transition joints are suited for all voltage levels, construction and insulation materials of cables. A one core cable can be safely connected to a three core cable through this joint. They act as important medium for connecting the old paper-insulated cable technology with polymeric cables. Straight Joints: This type proves useful when a need is felt for extending cable pieces in any application. They are suited for outdoor, indoor, underground and submerged cable jointing.
Pot End Joints: These types of joints are used in situations which require secure termination of power cables that are liveand need to be abandoned temporarily or on a permanent basis for some reason or the other.
Concluding
Cable joints act as safe means for undertaking electrical connections between several cables and as such need to adhere to the standards set by the industrial associations.